Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If e^f(x) = 10 x/10 x, x∈ ( 10,10) and f(x) = kf ( 0x/100 x^2 ) then k =Rappelons que par exemple 5!Se lit "factorielle 5" et est égal à 1 x 2 x 3 x 4 x 5 Par cette formule, il obtient une estimation de e avec 18 décimales exactes Nous devons aussi à Euler la démonstration de l'irrationalité de e 2) Propriétés Propriétés Pour tout réel x et y, on a a) et b) c) d) e)

A Refer To The Trapezoid Efgh With Median Overli Gauthmath
If f(x)=e^-1/x^2 x 0
If f(x)=e^-1/x^2 x 0-If f(x) = ln((x2 e/x2 1)), then range of f(x) is If f(x) = ln((x2 e/x2 1)), then range of f(x) is (A) (0, 1) (B) (0, 1 0, 1) (D) 0, 1 Check Answer and Solution for above question from Mathem If f(x) = ln((x2 e/x2 1)), then range of f(x) is (A) (0, 1) (B) (0, 1 0, 1) (D) 0, 1Connect English ©21 Wolfram Alpha




Solved Consider The Piecewise Function F X X2 2x 1 Chegg Com
· Lets show that f ( x) = x 3 is injective We take general x, y ∈ R For them we say that f ( x) = f ( y) Then we know what f does to them and we will get x 3 = y 3 Applying the thirdroot will give us x = y That means that f ( x) = x 3 is injective The same argument wont work with f ( x) = xIf e^x e^f (x) = e , then range of the function of f (x) is maths13 We have 1 E F n!
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If f (x) = x 1/x 1 ( x ≠± 1 ) then find i) (fofof)(x) ii) (fofofof)(x)Cannot be improved 14 TFTTTFFTT 15 Let F = Q and E = Q(p 2) Then f(x)=x4 5x2 6=(x2 2)(x2 3) has a zero in E, but does not split in E 16F (x)=\frac {1} {x^2} y=\frac {x} {x^26x8} f (x)=\sqrt {x3} f (x)=\cos (2x5) f (x)=\sin (3x) functionscalculator f\left (x\right)=\frac {1} {x^2} en
2 y x = 1 Explanation f (x) = (2 x − 2) e 2 x − 2 ⇒ f ′ (x) = (4 x − 2) ⋅ e 2 x − 2 If \displaystyle{f{{\left({x}\right)}}}={e}^{{{2}{x}{4}}} and \displaystyle{g{{\left({x}\right)}}}={\tan{{3}}}{x} , what is \displaystyle{f}'{\left({g{{\left({x}\right)}}}\right)} ?X23(x4−1) View solution steps Short Solution Steps f ( x ) = 3 x ^ { 2 } \frac { 3 } { x ^ { 2 } } f ( x) = 3 x 2 − x 2 3 To add or subtract expressions, expand them to make their denominators the same Multiply 3x^ {2} times \frac {x^ {2}} {x^ {2}}Démontrer que H est une primitive sur R de la fonction h définie par h(x)=xe−x 2) On note D le domaine délimité par la courbe C,ladroiteT et les droites d'équation x = 1 et x = 3 Calculer, en unité d'aire, l'aire du domaine D http //wwwmathsfrancefr 1 ⃝c JeanLouis Rouget, 14 Tous droits réservés Antilles Guyane 14 Enseignement spécifique EXERCICE 2




If Ig X Hg 8 And Ef 12 What Is The Value Of X Brainly Ph




Misc 15 Let F X X2 X G X 2 X 1 2 1 Are F G
F (x)=2 (x1)^2 Calculadora de funções Symbolab Equações de reta Reta Dois pontos Ponto e inclinação Inclinação Forma inclinaçãointercepto Distância Ponto médioPar k(x) = ex3 – x 1 Exercice 10 Déterminer la dérivée de chacune des fonctions définies cidessous en précisant dans chaque cas l'ensemble de validité des calculs a) f(x) = ex b) g(x) = e2x – 3ex 4 c) h(x) = (x 1)ex d) k(x) = exp 1 x e) m(x) = ln(3 ex) Exercice 11 Valider ou) if p X(x) = 1 ( ) x 1e x= for x>0 where ( ) = R 1 0 1 x 1e x= dx Remark In all of the above, make sure you understand the di
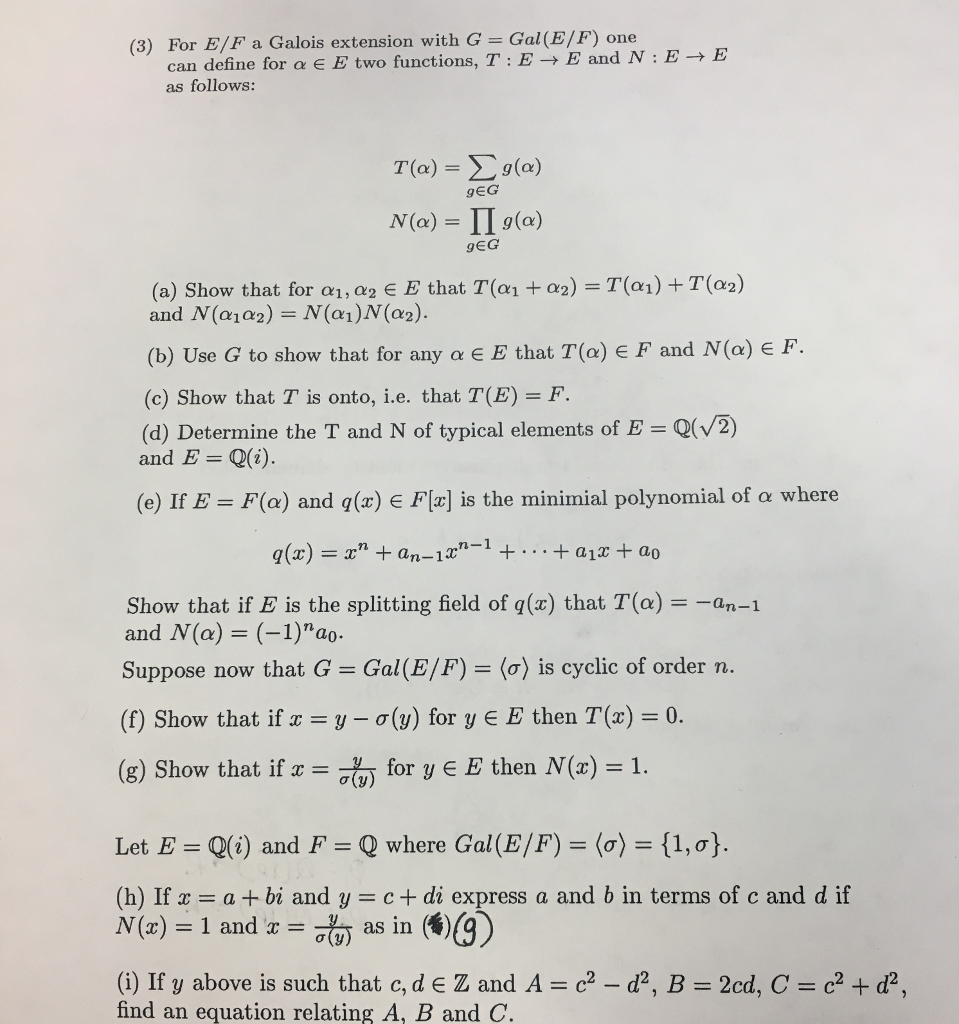



Solved 3 For E F A Galois Extension With G Gal E F O Chegg Com



Differentiation Ppt Download
Log plot x^2 plot arctan(x^2, 1/x^2) polar plot Re((e^(i phi))^2) solve x^2 using Newton's method with x0=2;In mathematics, the exponential function is the function f ( x ) = e x, {\displaystyle f(x)=e^{x},} where e = 2718 is Euler's constant More generally, an exponential function is a function of the form f ( x ) = a b x, {\displaystyle f(x)=ab^{x},} where b is a positive real number, and the argument x occurs as an exponent For real numbers c and d, a function of the form f ( x ) = a b c x d {\displaystyle f(xY > 0 and F(t) = ∫ f(t y) g(y) for (x → 0,t) dy, then asked Oct 12, 18 in Mathematics by Samantha (3k points) integral calculus;




Indefinite Integral Of 1 X Antiderivative Of 1 X Video Khan Academy




If F X E X E X 2 Then Inverse Of F X Is
This equation is in standard form a x 2 b x c = 0 Substitute f for a, f − 1 for b, and 1 for c in the quadratic formula, 2 a − b ± b 2 − 4 a c x=\frac {\left (f1\right)±\sqrt {\left (f1\right)^ {2}4f}} {2f} x = 2 f − ( f − 1) ± ( f − 1) 2 − 4 f Take the square root of \left (f1\right)^ {2}4f · re Equation différentielle avec du f (1/x) à 1725 salut en posant x=1/t et en remplaçant dans l'équation et en isolant f' on a f' (1/x)= (1/2) 2 f (x)1 Posté par carpediem re Equation différentielle avec du f (1/x) à 1727 f' (1/x)= (1/2) x 2 f (x)1 · relations and functions jee jee main 0votes 1answer Let f (x) = (x 1)(x 2)(x 3)(x 4) 5 , where x ∈ 6, 6 If the range of the function is a, b where a b, ∈N, askedDec 6, 19in Sets, relations and functionsby RiteshBharti(538kpoints) sets




Solved Consider The Piecewise Function F X X2 2x 1 Chegg Com



Lecture 15 1 Expectations 2 Covariance And Correlation
Answer to If f(x) = (x 1)/(x^2 2), find A) f(1) B) f(a 1) C) f(a 1) D) f(a 1) f(a) E) f(a 1) f(a 1) By signing up, you'llSe lit "factorielle 5" et est égal à 1 x 2 x 3 x 4 x 5 Par cette formule, il obtient une estimation de e avec 18 décimales exactes Nous devons aussi à Euler la démonstration de l'irrationalité de e Avec cette nouvelle notation, on peut ainsi résumer l'ensemble des propriétés de la fonction exponentielle Propriétés Pour tous réels x et y, on aContact Pro Premium Expert Support » Give us your feedback » Pro;




A Refer To The Trapezoid Efgh With Median Overli Gauthmath




If F X Cos 1 1 Logx 2 1 Logx 2 Then The Value Of F E Is Equal To Youtube
1 p x2 y2 z2, (e) f(x,y) = 4y (x2 1), (f) f(x,y,z) = sin(x)ey ln(z) Section 3 Directional Derivatives 7 3 Directional Derivatives To interpret the gradient of a scalar field ∇f(x,y,z) = ∂f ∂x i ∂f ∂y j ∂f ∂z k, note that its component in the i direction is the partial derivative of f with respect to x This is the rate of change of f in the x direction since y and z areOne way of solving is f(x) = log(1x/1x) f(x) = log(1x) log(1x) To find the given function replace x with (2x/1x^2) f(2x/1x^2) = log(1(2x/1x^2)) log(1(2x/1x^2)) f(2x/1x^2) = log((x^212x)/(1x^2))log((x^212x)/(1x^2)) On simpli · Let I1 = ∫Xf{x(2 x)} x∈sin2t, 1 cos2t dx and I2 = ∫f{X(2 x)} asked Sep 10, 19 in Mathematics by Juhy (631k points) integral calculus;




If F X X 3 4x 1 Find F 3




If F X E 2x 1 4x 1 2 Ln 1 X 2 For X 0 Then
Et 1 0 J (2x 1)e2xdx Exercice13 On se propose de chercher les solutions U définies et dérivables sur telles que pour tout reel x ex U x U x 1 '( ) ( ) 1 1 1/Soit f la function définie sur par x x e f (x) ln(1 e) Verifier que f est une solution de 1X {\displaystyle X} The expected value is also known as the expectation, mathematical expectation, mean, average, or first moment Expected value is a key concept in economics, finance, and many other subjects By definition, the expected value of a constant random variable X = c {\displaystyle X=c} is · e^y = 1x^2 e^y y' = 2x y' = 2x/e^y = 2x/(1x^2) or, since e^y = 1x^2 y = ln(1x^2) y' = 2x/(1x^2)




If F 1 4 F 1 2 Then Find The Value Of Derivative Of Log F




Abcd Is A Trapezoid With Median Ef Brainly Ph
Exercice Comparer graphiquement deux images d'une fonction Exercice Donner les coordonnées des points d'intersection de deux courbes Exercice Résoudre graphiquement une équation du type f (x)=k Exercice Étudier la position relative de deux courbes Exercice Résoudre graphiquement une inéquation du type f (x)0 votes 1 answer lf f(y) = e^y, g(y) = y;Rappelons que par exemple 5!




If The Function F X 2 E X And G X F 1 X Then The Value




Answered Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Bartleby
· Let's use our original identity, that f(g(x))=x, for all x f(g(1))=1 g^3(1)e^(g(1)/2) = 1 To make this equality simpler to look at, let u = g(1) u^3 e^(u/2) = 1 Well, you might be able to see that u=0 is a solution of this equation But how do we prove it's the only one?This equation is in standard form a x 2 b x c = 0 Substitute 1 for a, f − 2 for b, and f for c in the quadratic formula, 2 a − b ± b 2 − 4 a c x=\frac {\left (f2\right)±\sqrt {\left (f2\right)^ {2}4f}} {2} x = 2 − ( f − 2) ± ( f − 2) 2 − 4 f Take the square root of \left (f2\right)^ {2}4fWell, it's clear that the function is monotonically increasing This is because, as x gets bigger and bigger, so does f(x) This makes u=0 the only solution color(blue)(g(1




Pdf Some Remarks On Soft Jp Open Sets In Soft Topological Spaces



Ex 5 1 29 Find K F X Kx 1 3x 5 Is Continuous At X 5
· Ex 13, 6 Show that f −1, 1 → R, given by f(x) = 𝑥/(𝑥 2) is oneone Find the inverse of the function f −1, 1 → Range f (Hint For y ∈ RangeSteps Using Derivative Rule for Sum f ( x ) = 3 x ^ { 2 } 1 f ( x) = 3 x 2 1 The derivative of a polynomial is the sum of the derivatives of its terms The derivative of a constant term is 0 The derivative of ax^ {n} is nax^ {n1} The derivative of a polynomial is the sum ofWelcome to Sarthaks eConnect A
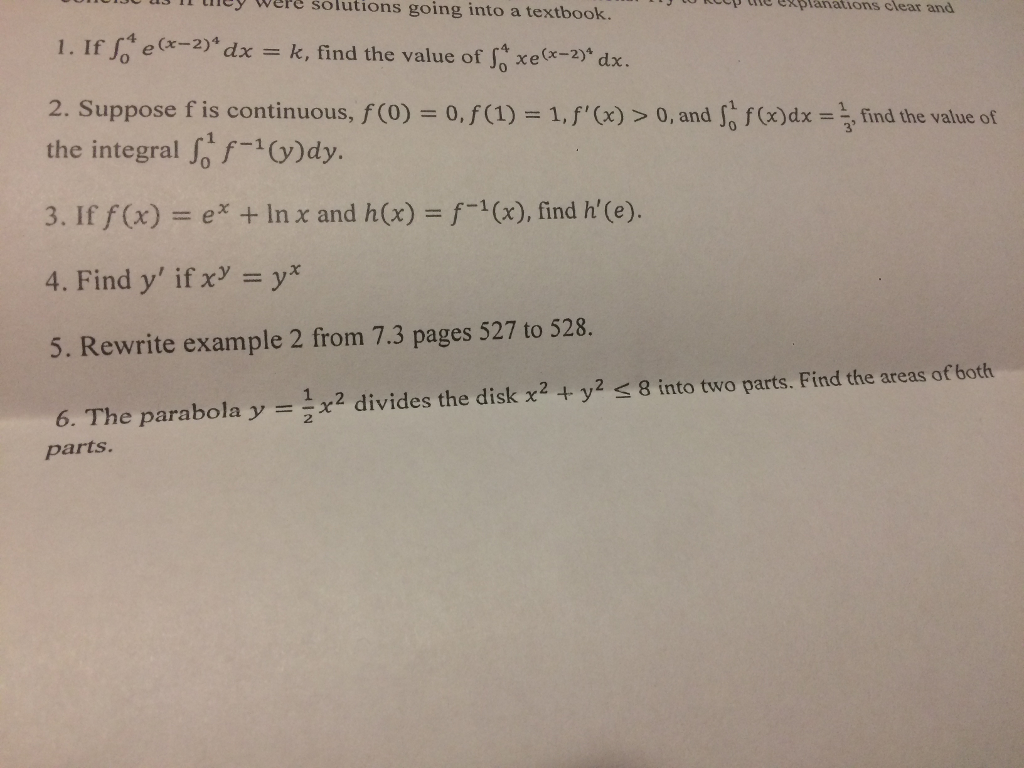



If Integral 4 0 E X 2 4 Dx K Find The Value Of Chegg Com




If F X E X 1 E X I 1 Int F A F A Xg X 1 X Dx And I 2 I
To find E f(X) , where f(X) is a function of X, use the following formula E f(X) = S f(x)P(X = x) Example For the above experiment (with the die), calculate E(X 2) Using our notation above, f(x) = x 2 f(1) = 1, f(2) = 4, f(3) = 9, f(4) = 16, f(5) = 25, f(6) = 36 P(X = 1) = 1/6, P(X = 2) = 1/6, etc So E(X 2) = 1/6 4/6 9/6 16/6 25/6 36/6 = 91/6 = The expected value of) Gamma X˘( ; · Soit f(x) = x² 6x 1 et g(x)= 2x 6 Les deux définies sur R On a montrer que pour tout réel x, f(x)g(x) = (x2)² 9 On me demande de calculez les points d'intersection des courbes de f(x) et de g(x) Je vois les points d'intersection sur le graphique que j'ai tracé mais j'ignore comment les calculez




Strong Convergence Theorems For Families Of Weak Relatively Nonexpansive Mappings Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub




Solve This B C D E X2a X 1 Find F If F X Find If F X Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com
The example E = F = Q and f(x)=x2 1 shows that the lower bound 1 cannot be improved unless we are told that f(x) is irreducible over F Example 509 shows that the upper bound n! · The given equation is e x e f (x) = e ⇒ e x = ee f (x) taking " log " on both sides, we get ⇒ ln e x = ln ee f (x) ⇒ x = ln ee f (x) Now, we have calculated x in terms of f (x), and now the domain of R H S will be the range of function Now, " log " cannot take negative values, so, ee f (x) > 0 ⇒ e 1 > e f x ⇒ 1 > f x or f x < 1 Thus, range will be ∞, 1N1x n1 a n2x n2 a 1x a 0 On définit d°(P) = n (la plus grande puissance de x) 2) Fonctions rationnelles Déf Fonction rationnelle = Fonction polynôme Fonction Polynôme 3) Fonctions homographiques Déf Soit a, b, c et d 4 réels non tous nuls et tels que c et d ne sont pas nuls ensemble On appelle fonction homographique la fonction f définie par ax b cx d



greer105examsoln5 Jpg




If Int X 1 X 2 E X Dx F X E X C Then Write The Value Of
· #"differentiate using the "color(blue)"product rule"# #"given "y=g(x)h(x)" then"# #dy/dx=g(x)h'(x)h(x)g'(x)larr" product rule"# #g(x)=x1rArrg'(x)=1#X21 b Calculer ∫ 1 e f(x)dx a On met au même dénominateur 1 x x x21 = x21x ×x x(x21) =f(x) b∫ 1 e f(x)dx=∫ 1 e 1 x x x21 dx=ln(x) 1 2 ln(x21) e =1 1 2 ln(e21)− 1 2 ln(2) en remarquant que le second morceau de la somme est sous la forme 1 2 u' u Complexes 13Résoudre dans ℂ l'équation z2−2z 4=0 et donner l'écriture exponentielle des solutions Il suffit · Let y = f (x) Then, y = x2 − 1 To determine the inverse function, switch the places of x and y, and subsequently solve for y x = y2 − 1 y2 = x 1 y = ± √x 1 Since this is the inverse, y = f −1(x) f −1(x) = ± √x 1




Grf1 J Through Hole Vertical Footprint Datasheet By Samtec Inc Digi Key Electronics
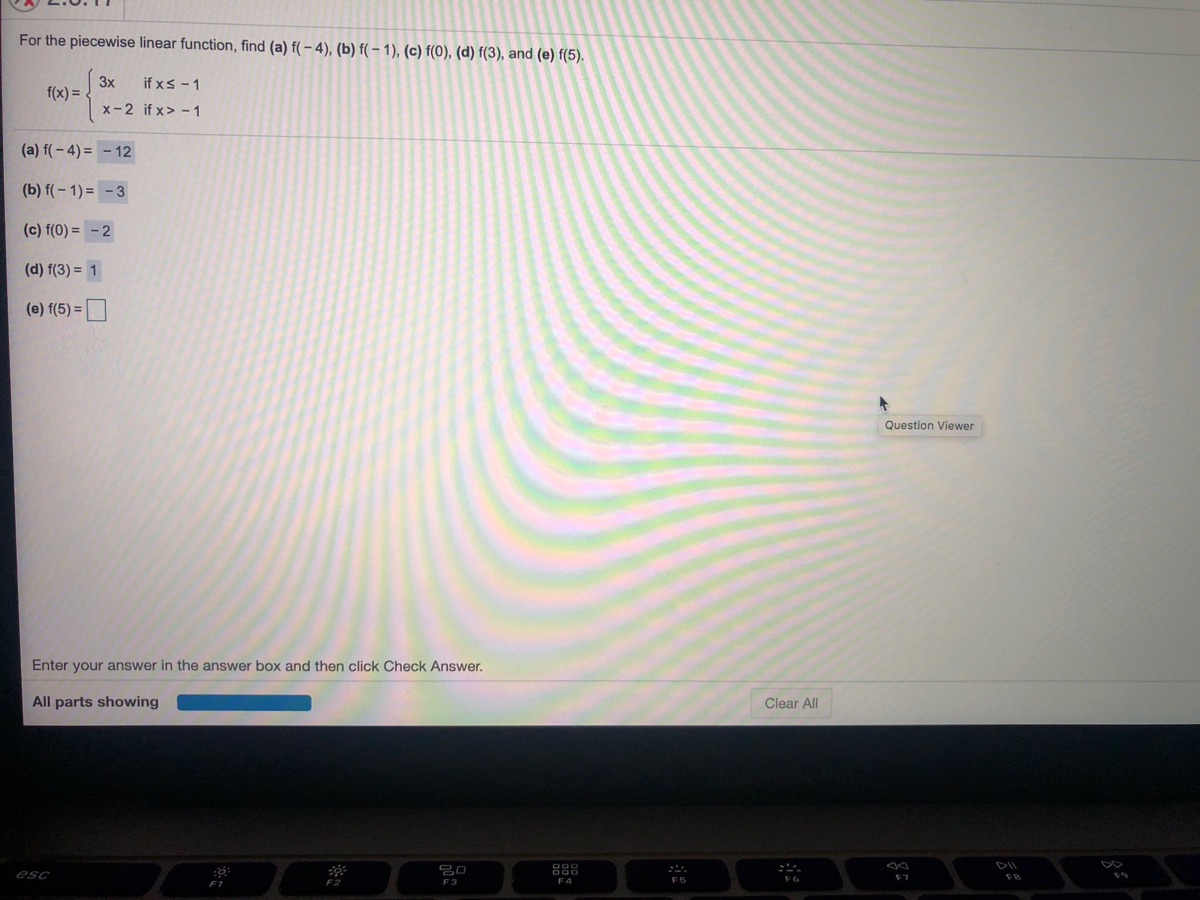



Answered For The Piecewise Linear Function Find Bartleby
· Define function Define bijective function Let defined by f (1) = f (2) = 1 and f (x) = x – 1 for x > 2 Show that f is onto but not oneone Check the function given by is oneone or not Queries asked on Sunday & after 7pm from Monday to Saturday will be answered after 12pm the next working dayHave a question about using WolframAlpha?API & Developer Solutions;




On The Existence Of Fixed Points That Belong To The Zero Set Of A Certain Function Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On




If F X X 1 Tan 1 E 2x Then F 0 Is
If f (x) = (a b − b 2 − 2) x ∫ 0 1 (cos 4 θ sin 4 θ) d θ is decreasing function of x all x ∈ R and b ∈ R being iindependent of x, then Hard View solutionN otation f E → F, e nsemble de définition d'une fonction (niveau lycée) Écrire f(x) = x 2 1/x est imprécis tant que l'ensemble dans lequel varie x ainsi que sa plage de variation n'est pas précisée A priori, le plus large champ de variation de x est ici R privé de 0 car la division par zéro n'a pas de sens !X= (X 1;X 2;;X k) be the count of the number of balls of each color drawn We say that Xhas a Multinomial (n;p) distribution The pdf is p(x) = n x 1;;x k px 1 1p x k k Exponential X˘exp( 1) if p X(x) = e x= , x>0 Note that exp( ) = (1 ;




If F X X 2x Find The Value Of F 1 E 1 2 Chegg Com




Why If F X 0 Then X In E 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange
F(x) est ainsi calculable sur R* = ∞,0∪0,∞ Lors de lCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyGn(x)=1xx2 ···xn et hn(x)=12x···nxn−1 1 Vérifierque,pourtoutréelx (1−x)gn(x)=1−xn1 Onobtientalors,pourtoutréelx ̸=1 gn(x)= 1−xn1 1−x 2 Comparerlesfonctionsh netg′,g′ étantladérivéedelafonctiongn Endéduireque,pourtoutréelx ̸=1 hn(x)= nxn1 −(n1)xn 1 (1−x)2 3




Derivative Wikipedia



Solved Old Bisect Each Other Written Math Quot A Abcd Is A Trapezoid With Median Ef D E A B 16 If Dc 2x 10 Ab 3x And Ef 4x What Course Hero
4 x a (3x2 – 1)exp(x3 – x 1) est la dérivée de la fonction k définie sur !1 e f(x;y) = 2(1ˆ 2) (x X)2 ˙2 X ( y Y) 2 2 Y 2ˆ(x x)(y ) ˙x˙y 2ˇ˙ X ˙ Y p 1 ˆ 2 For this distribution, the marginal distributions for Xand Y are normal and the correlation between Xand Y is ˆ In the gures below we used R to simulate the distribution for various values of ˆ Individually Xand Y are standard normal, ie X = Y = 0 and ˙ X = ˙ Y = 1 The gures show scatter




F X 3 X 3 X Sgn E X 2 Where Sgn X Denotes Signum Function Of X Then Which One Of T Youtube
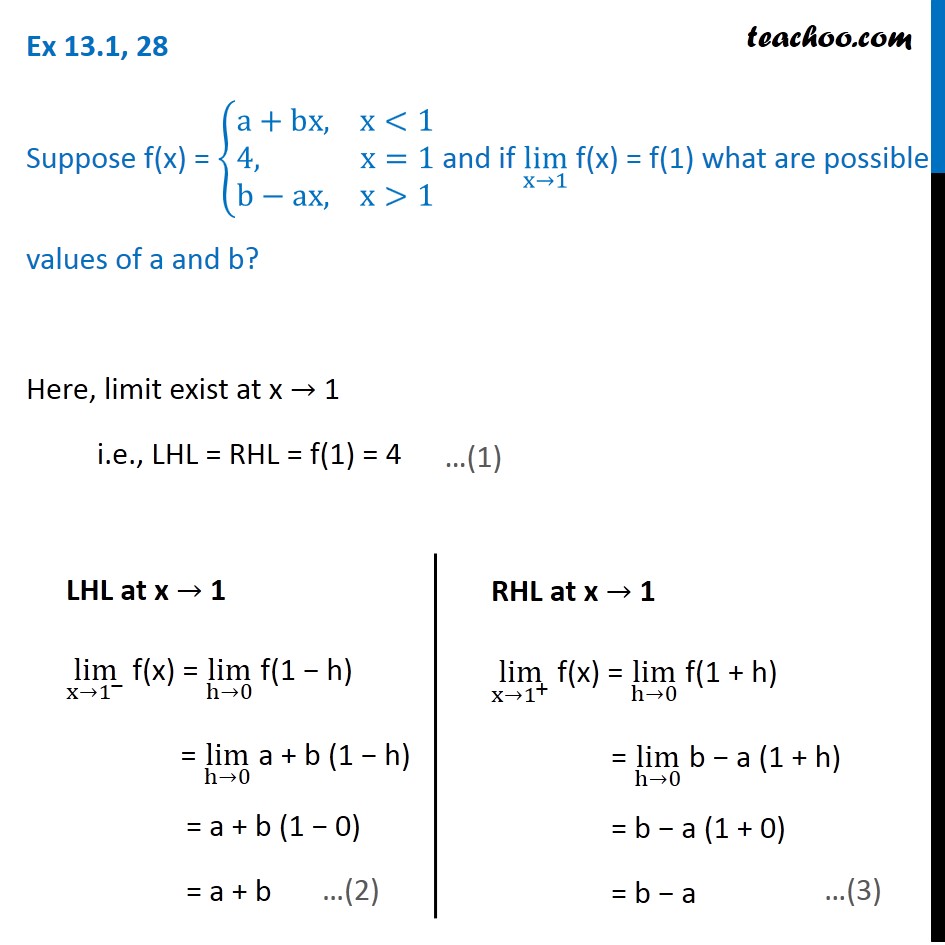



Ex 13 1 28 If Lim X 1 F X F 1 What Are Possible Values Of A




Answered Section 2 5 Continuity 125 X 2 If X Bartleby




Pdf On The Solvability Of P D F G For Vector Valued Functions




Field Fundamentals Chapter Field Extensions Definitions Lemma Pdf Free Download



Solved 3 Suppose F 2 3 And F 2 1 A If J X F X2 X Compute J 1 B If E 2 In F X 2 Compute 2 4 Suppose F X I Course Hero




Problems Chapter 4 Differentiation
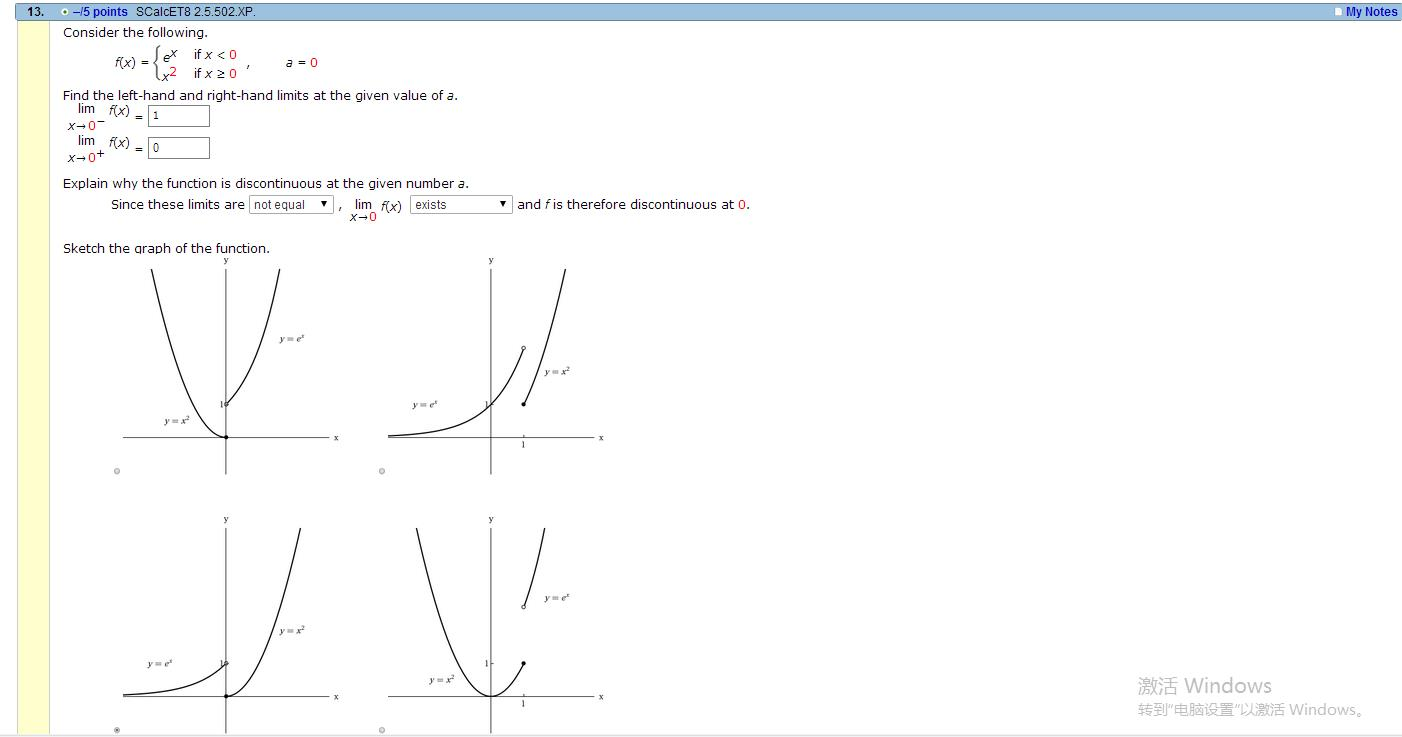



Solved Consider The Following F X E X X 2 If X 0 I Chegg Com




If F X E 1 X 2 X 0 And F X 0 X 0 Then F X Is




E Mathematical Constant Wikipedia




If F X X 2 E 1 X X 0 K X 0 Is Continuous At X 0 Wh




Bioinformatics Msc Mathematics Probability And Statistics D A Stephens Department Of Mathematics Imperial College London Pdf Free Download
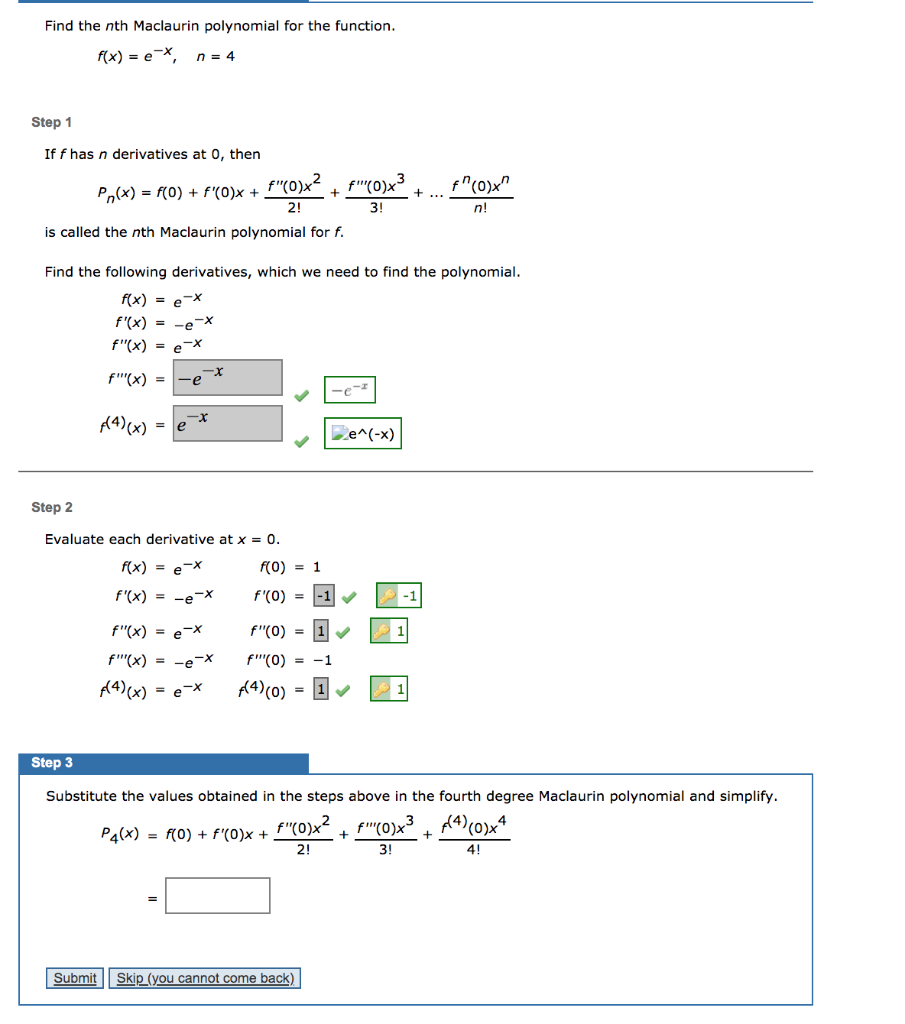



Find The Nth Maclaurin Polynomial For The Function Chegg Com




If F R 0 2 Defined By F X E X E Xe X E X 1 Is Invertible Find F 1




What Is F X Int X 2 2x E X 1 Dx If F 2 4 Socratic




If F X X 2x Find The Value Of F 1 E 1 2 Chegg Com




If F X E Xg X G 0 2 G 0 1 Then F 0 Is Equal To Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿